Privilege Escalation On Windows
Many security vulnerabilities exist in Microsoft Windows, and new ones are being found constantly. This article explains how to add a new user on Windows though an exploit which already exists for years.
This user has administrator rights and was created without the help of an existing administrator user. This method can also be used to reset the password of a local user when locked out of the computer. So not every still usable exploit is bad.
How it works
Preparations
As a preparation, a boot stick with the live version of the Linux distribution Kali Linux was created. There are many good programs out there to create a boot stick, but in this example Rufus has been used.
I. Disable Secure Boot
To boot from our boot stick, we may first have to disable the secure boot of the computer. Restart the computer and boot into the BIOS by holding down a specific key during start up. What key can vary from producer to producer. If the key is unknown it is a good to start with the keys F10, F2, F12, F1, or DEL. If none of these work, you may also google for it.
In the BIOS, the Secure Boot option has to be disabled. The location of this setting again can vary from producer to producer.
Also, as we are already in the BIOS, the boot order has to be changed. This ensures that our live distribution we set up earlier will boot first. Find the boot configuration in the BIOS and set the USB Storage (or called similarly) as the topmost device.
If done so, exit the BIOS and let the computer restart. Plug in the USB device if not already done so, and the computer should now boot into the Linux distribution.
II. Live Linux Boot
If no mistakes have been made so far, the Linux distribution should start fine. Once loaded into the desktop environment, the File-Explorer can be opened and the Windows system partition selected.
If you now navigate to C:\Windows\System32, you can search for Utilman.exe there. This file is normally used to provide functionality such as the screen magnifier, on-screen keyboard or speech output in the Windows login screen. If this file is now renamed to e.g. Utilman.exe_, then any other file can be executed instead of the Utility Manager. The new file is then started with system rights. In this case, the new file is cmd.exe. If this is copied and renamed to Utilman.exe, it is possible to open a command prompt in the Windows login screen with system privileges.
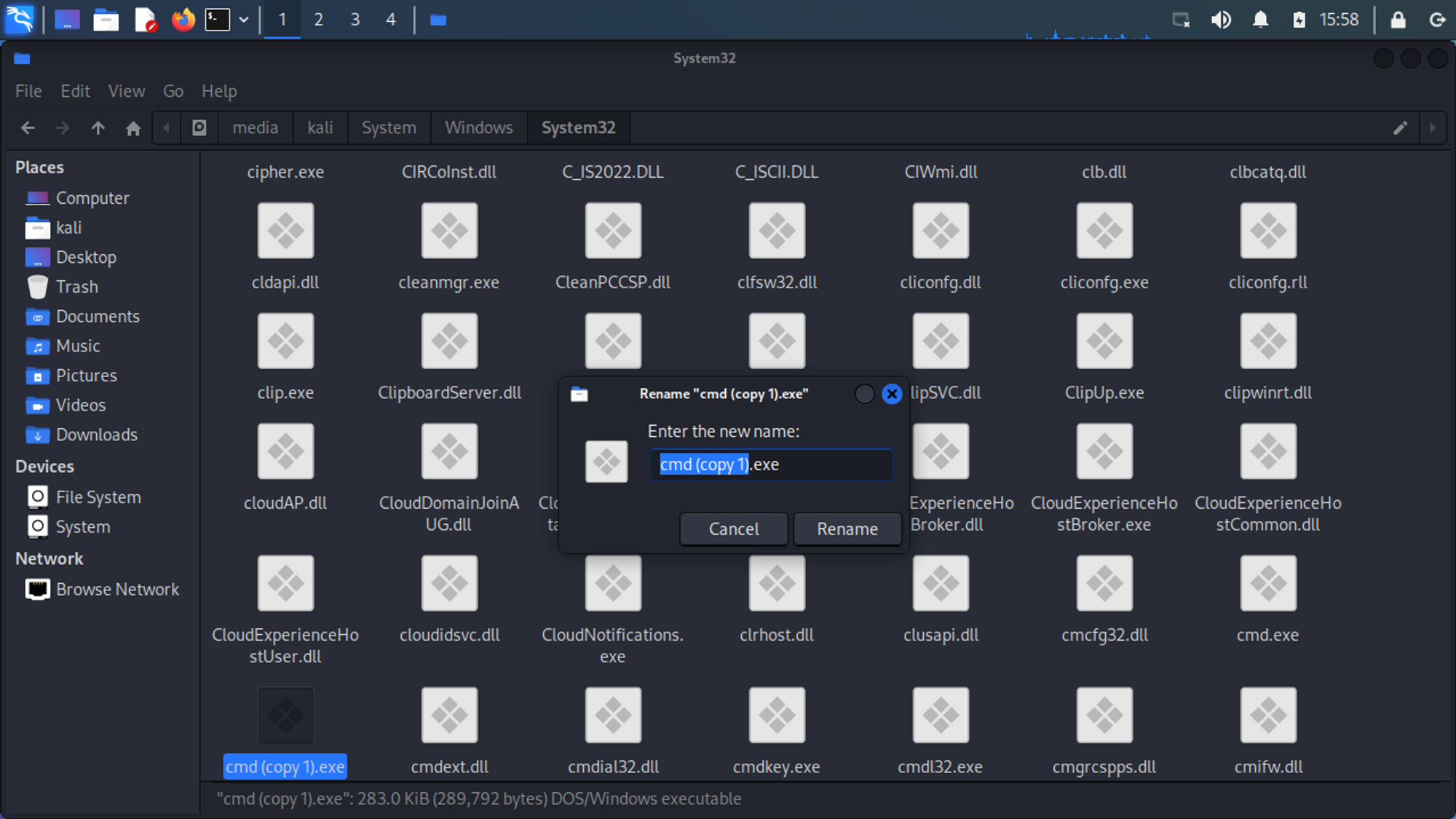
If the folders appear to be write-protected, try shutting down Windows completely. Some computers do not shut down Windows completely when clicking Shutdown on Windows to increase their startup time. To fix this, simply hold the Shift-Key pressed while clicking Shutdown, and Windows should shut down completely.
The Linux distribution can now be shut down, the boot stick removed, and the computer restarted.
III. Windows Login
If Windows is now started, the command prompt can be opened with system rights via the Utility Manager. These system rights can now be used to create a local administrator. This can be achieved with a few simple commands.
In this example, only a local administrator is created. But in a real scenario, these command could download a payload to the computer or similar.
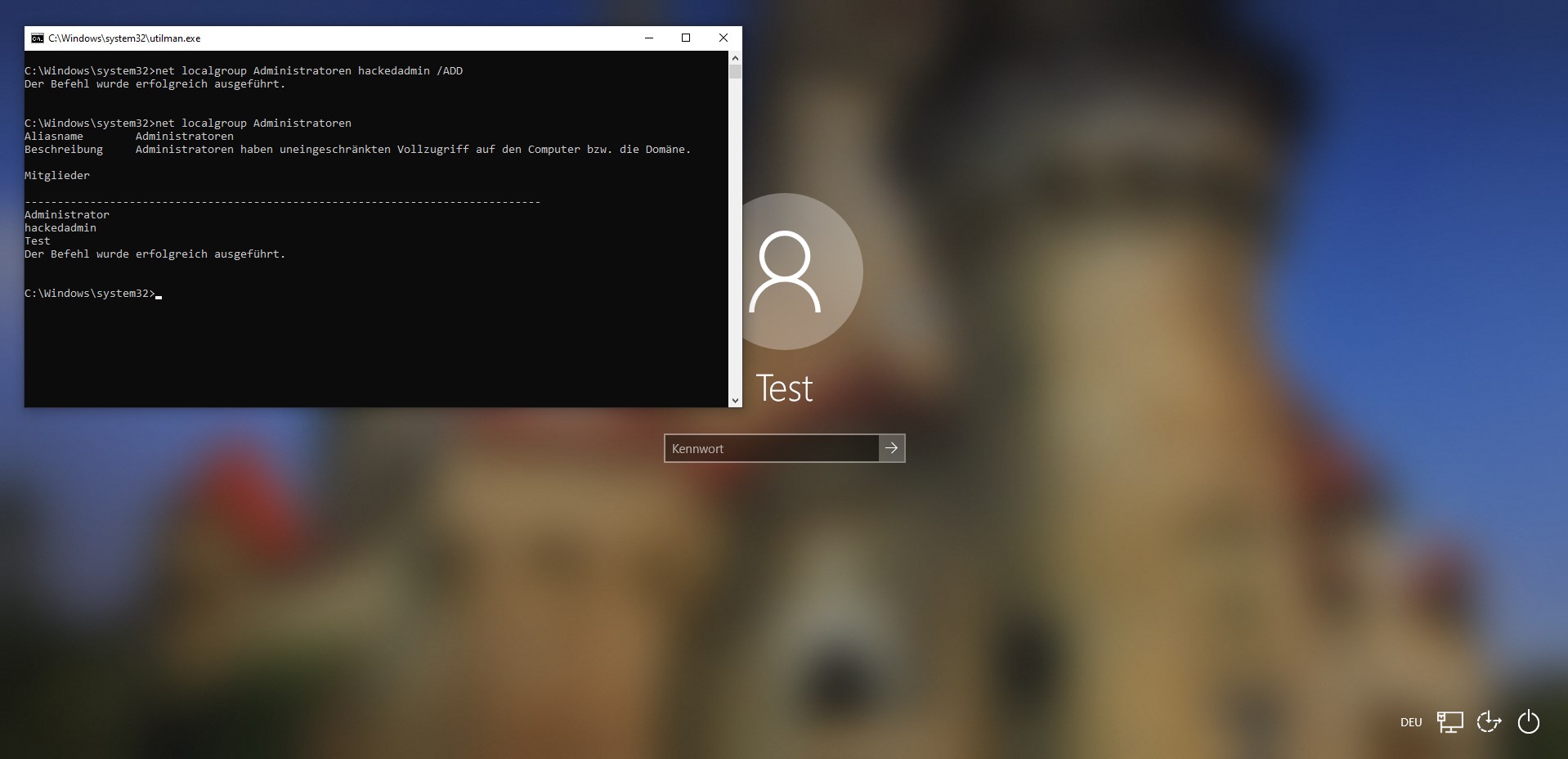
The command net user hackedadmin Admin1234! /ADD adds a new local user to the computer with the name hackedadmin and the password Admin1234!. Running this command should be successful.
If this was successful, the newly created user can be added to the administrators with the command net localgroup administrators hackedadmin /ADD. If the name of the Administrators group is not known, all available groups can be printed with the command net localgroup. Finally, net localgroup administrators can be used to check whether the newly created user is also an administrator.
This user can now also be used to log in under Other user.
However, if the computer is located in a domain it is important that the host name of the computer is written in front of the user (e.g.
ComputerName\Username), since the computer is located in a domain and the user will otherwise not be found by this domain. With the computer name in front of the username, Windows will see this as a local user.
Conclusion
If physical access to a computer is possible, it is almost impossible to protect against attack.
Hard Drive Encryption
However, encrypting the hard drive with BitLocker, for example, can help prevent a hard drive from being read directly in the event of loss. This should be used especially for portable devices like laptops.
BIOS Password
Also setting a password in the BIOS can help that the boot order, or other critical settings can not be changed.
Minimize Human Error
And last but not least, care should always be taken of the device itself. After all, physical access is only possible if the device is in someone else’s possession.
Article Sources
Add new user account from command line. Windows Command Line [Status 25/04/2022]
Add user to group from command line. Windows Command Line [Status 25/04/2022]
List of user groups command line. Windows Command Line [Status 25/04/2022]
How to Enter BIOS Setup on Windows PCs. HP [Status 25/04/2022]
Administrator-Passwort zurücksetzen. Ionos [Status 25/04/2022]